Understanding power delivery on the motherboard is crucial when building or upgrading a computer.
Power stages on a motherboard manage power delivery to the CPU by stabilizing voltage. They consist of transistors, chokes, and capacitors, ensuring stable power, lower temperatures, and better overall system performance, especially during heavy tasks like overclocking.
In this article, we’ll break down the importance of power stages, explain the different types, and help you choose the correct motherboard for your needs.
Understanding Power Delivery on a Motherboard
Power delivery is how a motherboard distributes electricity to critical parts like the CPU and GPU. This process ensures that every component gets just the right amount of power to work smoothly, stay stable, and avoid overheating. Good power delivery makes your PC reliable and efficient.
Motherboard VRMs

VRMs, or Voltage Regulator Modules, are like power managers on your motherboard. They control how electricity flows to your CPU and other parts, ensuring steady and safe power.
Good VRMs improve performance, prevent overheating, and support overclocking, making your computer faster and more stable during heavy use.
Importance of Efficient Power Delivery
1. Stability
Stable power delivery avoids sudden shutdowns and system errors. It keeps your PC reliable, even during demanding tasks like gaming or video editing, ensuring everything works without interruptions.
2. Longevity
Efficient power extends the lifespan of your components. Delivering steady and clean electricity reduces wear and tear, helping your computer last longer and perform better over time.
3. Overclocking
Stable power is key to overclocking. It ensures your CPU and GPU can safely run faster than usual, giving you better performance without risking overheating or instability.
4. Performance
Clean, stable power boosts your PC’s performance. With consistent power, your system avoids lags and crashes, making tasks like gaming, editing, or multitasking smoother and faster.
5. Energy Efficiency
Energy-efficient power delivery reduces waste, saves on electricity costs, and lowers heat output. It’s better for your wallet and keeps your system cooler and more eco-friendly.
Also Read: AM5 Motherboard Tier List – Best Picks For Every Budget!
Types of Power Stages
1. Analog Power Stages
Analog power stages use simple circuits for steady power delivery. They’re affordable and reliable, making them great for basic tasks but less ideal for high-performance or demanding workloads.
2. Digital Power Stages
Digital power stages offer precise power control. They’re designed for heavy workloads, gaming, and overclocking, ensuring your PC runs efficiently, even under pressure.
3. Integrated Power Stages
Integrated power stages combine everything into a compact design. They save space on the motherboard while delivering efficient and stable power for a smooth computing experience.
4. Discrete Power Stages
Discrete power stages are separate components that offer higher performance. They’re popular among enthusiasts and overclockers looking for flexibility and superior power delivery.
5. Hybrid Power Stages
Hybrid power stages mix analog and digital technologies. They balance simplicity and precision, making them versatile for reliable and efficient power delivery.
Factors Affecting Power Stage Quality

- Component Materials: High-quality materials ensure durability and better heat management.
- Design and Layout: A well-designed power stage layout improves efficiency and reduces electrical interference.
- Power Rating: Higher-rated power stages handle more load and improve performance.
- Cooling Solutions: Effective cooling ensures stable operation and a longer lifespan.
- Brand Reputation: Trusted brands often provide better reliability and warranty support.
Impact on Performance and Efficiency
1. Stable Performance
Stable power delivery helps prevent sudden crashes and slowdowns. It keeps components like the CPU and GPU running smoothly, especially under heavy workloads like gaming or video editing, ensuring reliable performance.
2. Optimized Power Efficiency
Optimizing power delivery reduces energy waste, keeps heat levels low, and saves electricity. Efficient power management makes your system more environmentally friendly and cost-effective while maintaining strong performance.
3. Enhanced Overclocking Capability
High-quality power stages help when overclocking your components. By providing steady voltage, they prevent instability, allowing your CPU or GPU to perform beyond default limits without overheating or crashing.
Choosing the Right Motherboard Based on Power Stages
When selecting a motherboard, look for quality power stages that match your needs. A motherboard with good power delivery ensures stability, efficiency, and better performance.
Choose a motherboard with more power phases for demanding tasks like gaming or overclocking for reliable, sustained power.
Must Read: Motherboard Ethernet Drivers – Fix Ethernet Driver Issues!
How Does a VRM Enhance Performance?
A VRM ensures that your CPU and other components get stable power, preventing fluctuations that can cause slowdowns or crashes.
This leads to smoother performance, especially during heavy tasks like gaming or multitasking, enhancing overall system reliability.
What are the Benefits of Having Several Power Phases?
Several power phases help distribute power evenly across components, reducing stress and heat. More phases also improve stability, allowing for better performance, especially under heavy loads or when overclocking, and preventing system instability or damage.
How Many VRMs Are There on a Motherboard?
1. Visual Inspection
You can visually inspect VRMs by looking at the motherboard’s power phase components, which are often near the CPU socket. High-quality VRMs are usually larger and have heatsinks to keep them cool during use.
2. Motherboard Specification Sheet
The motherboard’s specification sheet lists the number of VRMs, power phases, and other features. This sheet helps you understand the motherboard’s power capabilities and ensures it meets your needs, especially for high-performance tasks.
What Are Power Phases?
Power phases refer to how the voltage is delivered to the CPU. More power phases allow better and more stable power distribution, reducing heat and improving efficiency. This is important for maintaining performance during heavy tasks like gaming or overclocking.
What Is Motherboard Power Phase?
Motherboard power phases manage how the electrical power is sent to the CPU and other components. A higher number of phases allows more stable power delivery, improving system stability and performance, especially during intense tasks like gaming or overclocking.
What Are Power Stages On A Motherboard Vrm
Power stages on a motherboard’s VRM (Voltage Regulator Module) help convert and distribute power efficiently to the CPU.
Each power stage manages a specific voltage, ensuring the CPU gets a steady, stable supply for optimal performance.
Teamed Power Stages Architecture – Asus
Asus’ teamed power stages combine multiple power stages to improve efficiency and reduce heat. This architecture allows for better load distribution across phases, enhancing overall power delivery to the CPU and resulting in more stable performance during demanding tasks.
Whats The Difference Between 14+2 And 12+2 Power Stage

A 14+2 power stage configuration has 14 phases for the CPU and 2 phases for other components, offering better performance and overclocking potential than a 12+2 setup, which has fewer phases and might not handle high loads as well.
What Are Power Phases And What Are Their Effects On Oc’ing
Power phases play a crucial role in overclocking (OC’ing) by delivering stable, reliable power to the CPU. More power phases allow for higher overclocking potential and better heat management, improving stability and performance when pushing the system beyond standard limits.
How Do I Read This New Nomenclature For Power Phases In A Mb?
The power phase nomenclature, like 14+2 or 12+2, indicates the number of phases for the CPU and other components.
The first number is for the CPU, and the second is for components like memory, providing insight into power delivery capabilities.
Z690: Do These Higher Power Phases Really Matter?
On the Z690 chipset, higher power phases (e.g., 16+1) matter for stability and overclocking. They provide better power delivery to the CPU and other components, ensuring smoother performance, especially for high-end processors and demanding workloads.
Motherboard Vrms: What Are Power Phases, And How Many Should I Have?
Power phases determine the stability and efficiency of power delivery to the CPU. More phases are better for stability, especially for high-performance CPUs. For most users, 6-8 phases are sufficient, but gamers or overclockers may benefit from more.
You Should Know: If I Replace My Motherboard Will I Lose My Data – Explore!
Technical Stuff: Power Phases
Power phases are part of a motherboard’s VRM (Voltage Regulator Module) and help distribute power to the CPU. More power phases provide better stability, less heat, and more efficient power delivery, improving overall system performance.
What Are The Differences Of Specific Power Stages (Drmos, Infenion Smart Power Stage, Etc.)
Different power stages, like DrMOS and Infineon Smart Power Stages, use various technologies for efficient power conversion. DrMOS is known for high efficiency and performance, while Infineon stages focus on stable voltage delivery and longevity.
About Vrms & Mosfets / Motherboard Safety With High-Tdp Processors
VRMs and MOSFETs work together to regulate and distribute power to the CPU. With high-TDP processors, a good VRM design prevents overheating and ensures stable performance by efficiently providing the right amount of energy, preventing damage to components.
What Is A Twin 16 Power Phase Layout?
A Twin 16 power phase layout uses 16 power phases dedicated to the CPU, split into two sets of 8 phases. This helps manage power more efficiently, improving CPU stability and allowing for higher overclocking potential.
4 + 1 + 1 Phase Power Design – What Does This Mean?
A 4 + 1 + 1 phase power design means 4 phases for the CPU, 1 phase for the memory, and 1 for the GPU. This setup balances power delivery to each component, ensuring good performance without excessive power strain on any part.
What Do 10+2, 5+3 Or 12 Power Phases On Motherboards On GPU Mean?
A 10+2 or 12-phase power design means the motherboard has 10 or 12 phases dedicated to the CPU and 2 or 3 for the GPU. More phases allow for better stability, especially for high-performance CPUs and GPUs.
Is 16+1 Power Stages Good?
Yes, a 16+1 power stage is excellent for stable power delivery to the CPU, ensuring efficiency and better overclocking potential. The additional phases for other components (like memory) help maintain system stability under heavy loads.
7+1+1 Power Phase
A 7+1+1 power phase design means 7 phases for the CPU and 1 for memory and GPU. This setup is standard in mid-range motherboards, offering a good balance of power efficiency, stability, and overall performance.
How Many Vrm Phases Do I Need
The number of VRM phases depends on your needs. For most users, 6-8 phases are sufficient. For heavy gaming, overclocking, or high-TDP processors, more phases (10 or more) will ensure better power delivery and system stability.
Four Phase Power Mode?
A four-phase power mode means the motherboard uses four phases to deliver power to the CPU. It’s a good balance for most systems, offering stability and efficiency for moderate gaming or productivity tasks.
Would Someone Explain Power Vrm Phases?
Power VRM phases manage the power distribution to the CPU. Each phase takes care of a part of the power supply, ensuring smooth and stable power flow, especially during heavy workloads or overclocking.
20+1 Power Stages
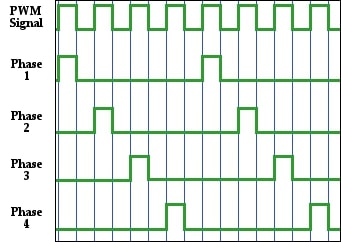
A 20+1 power stage refers to 20 phases dedicated to the CPU and one for another component. This setup ensures excellent power stability, especially for high-performance processors, and it also allows for better overclocking and heat management.
14+1+1 Power Phase
A 14+1+1 power phase means 14 phases for the CPU, 1 for memory, and 1 for the GPU. This setup balances power delivery for good overall system stability, particularly for gaming or demanding tasks.
Motherboard VRM Phases
Motherboard VRM phases are sections in the VRM that regulate and supply power to the CPU. More phases help evenly distribute power, enhancing system stability and preventing overheating during heavy tasks like gaming or overclocking.
How Many Power Phases for 13900K
For the Intel Core i9-13900K, at least a 16+1 or 18+1 power phase design is ideal. The 13900K is power-hungry, so more phases provide better power stability, especially under heavy workloads or overclocking.
Power Phases of Motherboards
Power phases in motherboards help manage how electricity flows to the CPU, memory, and other components. More phases provide smoother, more stable power, improving performance and longevity and reducing the chance of overheating.
Regarding Power Phases
Power phases control how power is delivered to your CPU. More phases lead to better performance, stability, and cooling. For demanding systems, choosing motherboards with more phases can result in smoother operation and reduced risk of instability.
How a Motherboard Handles Power?
A motherboard handles power through its VRM (Voltage Regulator Module), which regulates the power delivered to the CPU. It uses power phases to ensure a steady, efficient electricity supply, especially under load.
What are power stages on a motherboard MSI?
Power stages on an MSI motherboard regulate and deliver stable power to the CPU. High-quality power stages improve performance, stability, and cooling, ensuring smooth operation, especially during gaming or overclocking.
What are power stages in motherboards?
Power stages in motherboards manage voltage delivery to the CPU. They use components like transistors and capacitors to stabilize power, reduce heat, and improve system performance during demanding tasks like gaming or multitasking.
Are more VRM phases better?
More VRM phases improve power stability and heat distribution, making them ideal for overclocking and heavy workloads. They provide smoother performance and prevent overheating, ensuring reliable system operation even with power-hungry CPUs.
What does a power stage do?
A power stage converts and delivers electricity to your CPU at a stable voltage. This ensures efficient performance, reduced heat, and system stability, especially during demanding gaming or heavy computing tasks.
What is the phase sequence of a power system?
The phase sequence of a power system refers to the order in which electrical phases are delivered. It ensures smooth operation and balanced power delivery, which is critical for running devices efficiently without causing damage.
8+2+1 Power Phase
An 8+2+1 power phase means 8 phases for the CPU, 2 for memory, and 1 for the GPU. It balances power delivery, ensuring stable performance and reliable operation for gaming or multitasking.
Need To Know: USB-C Alt Mode Motherboard – Key Features and Uses In 2024!
How to spot decent VRM/phase power rather than marketing BS
Look for detailed specifications, such as the number of power phases, quality materials, and cooling solutions. Trusted brands with good reviews ensure reliable VRMs, while flashy claims without clear details are often just marketing gimmicks.
Are more power phases (VRM) on a motherboard means more overheating?
No, more power phases improve heat distribution, reducing stress on each phase. This helps prevent overheating and ensures better stability, especially for high-performance CPUs during gaming, multitasking, or overclocking.
Is 14+1+1 Enough for the 13700K, or Upgrade to 18+1?
A 14+1+1 power phase design is sufficient for the Intel Core i7-13700K. However, upgrading to an 18+1 setup provides more power stability, especially for overclocking or intensive tasks, improving overall performance.
FAQs
1. 12+2 Power Phase?
A 12+2 power phase means 12 phases for the CPU and 2 for other components, offering stable performance and reliable power distribution.
2. What is 14 50A 1 60A 1 Power Stages?
The 14 50A 1 60A 1 power stages indicate 14 50A phases for the CPU and 1 phase for the GPU.
3. Is 8 Phase VRM Good?
An 8-phase VRM is good for most systems, providing balanced power delivery, but may struggle with high-end overclocking.
4. How Do You Power Cycle a Motherboard?
To power cycle a motherboard, please turn off the PC, unplug it, wait a few minutes, and reconnect.
5. What Is the Power Phase of Z690?
Z690 motherboards typically feature high-end power phases, often around 12+1 or 16+1, designed for powerful CPUs.
6. Is Residential Power 1 Phase or 3 Phase?
Most residential power is 1-phase, supplying standard electricity to homes, while 3-phase is used for industrial purposes.
7. What Is the Difference Between NEMA 14-30 and 14-50R?
The NEMA 14-30 is for 30A appliances, while the 14-50R is for 50A appliances, commonly used for EV chargers.
8. What Is the Number of Stages in a Power Supply?
The number of stages in a power supply refers to the phases of voltage conversion, typically ranging from 1 to 10+.
9. What the Hell Is 8 Phase Power Design?
An 8-phase power design uses eight phases to regulate power to the CPU, improving stability and performance.
10. What’s the Deal with Power Phases?
Power phases distribute and regulate power to components like CPUs, ensuring stable, efficient performance, especially during demanding tasks.
Conclusion
In conclusion, power stages and VRMs are essential for stable and efficient power delivery to your motherboard’s CPU and components. A motherboard with more power phases ensures better performance, stability, and longevity, especially for high-demand tasks like gaming or overclocking.